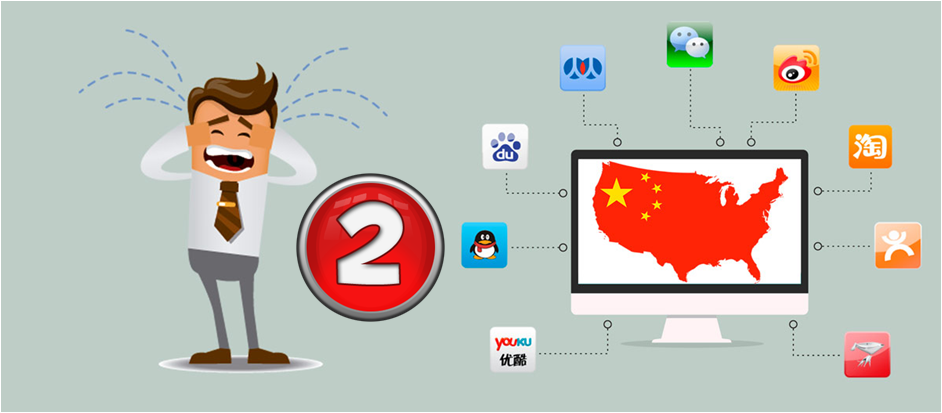
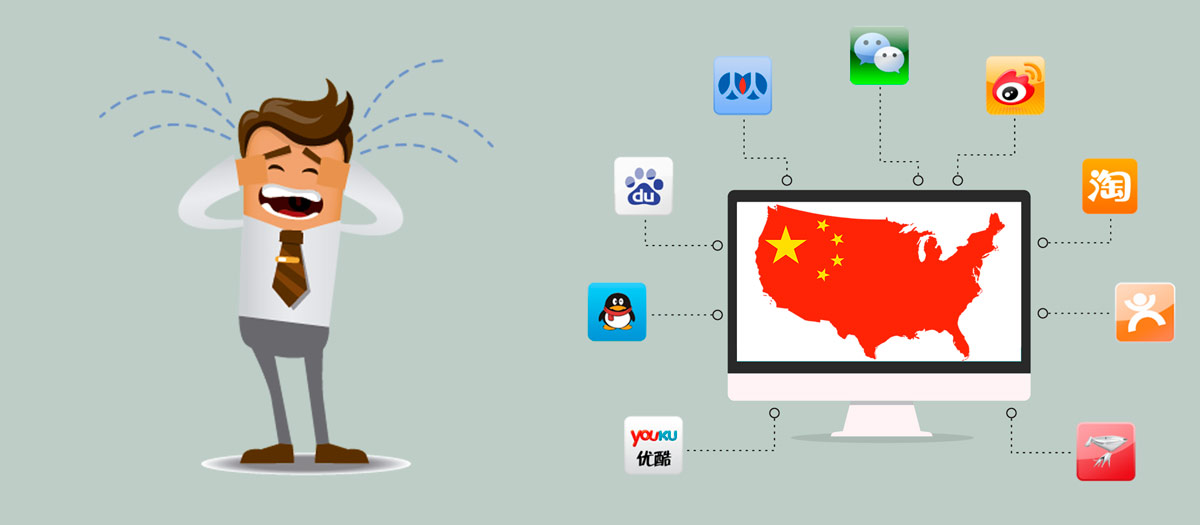
Infographic: 10 Things You Need To Know To Build a Chinese Website
A picture is worth a thousand words
After the great success achieved by our two articles 10 Things You Need To Know To Build a Chinese Website (I) (II), in the team we have thought it would be a good idea to summarize and turn them into an infographic.
We hope you enjoy it as much as we enjoyed its elaboration 🙂

Are you looking for a digital marketing and ecommerce agency?
Visit us. Let´s have a talk!
10 Things you Need to Know to Build a Chinese Website (Part 2)
In the first part of this article, we showed and identified 5 main points that differentiate a Chinese website from its western counterpart that we need to keep in mind in order to build a good one.
Let us summarize some of the main points addressed in the previous article:
- The style, design and structure are more complex and with much more information in opposition to the cleanness of the western websites
- In terms of user experience, Chinese are used to a great amount of links and keyword search boxes are the kings for navigation purposes
- Where to host your Chinese website is one of the first decisions to make. The most of the times we advise you to have a hosting in China. For that you will need a Chinese company to apply for an Internet Content Provider (ICP License)
- The Chinese Great Firewall blocks all websites that do not meet the content requirements that marks the Chinese government
- Your website needs to be ready to integrate with the main Chinese players. Google, Facebook and friends are banned in China; instead you will need to use the BATs (Baidu, Alibaba and Tencent).
After this little updating, we would like to further develop this post showing you 5 more crucial things to take in consideration when building a good Chinese website.
When building a chinese website, What else should I know?
6 – CHINA IS MOBILE. BE RESPONSIVE
Adapting our website to mobile is very important in any country, but in China is mandatory.
The Smartphone is, in many cases, the only way they have to access the Internet. Therefore Chinese users are much more familiar with the use of mobile devices. Keep in mind that almost the 50% of all Ecommerce transactions made in 2015 were done via mobile, compared to the also quite high 22% in the United States.
Don’t think any longer and start working on a nice mobile design… Mobile first!

7 – DOMAIN. WHICH ONE IS THE RIGHT OPTION FOR ME
In your approach to domains, three are the main options:
– Not that long ago, to have a .CN was a must. It was not possible to get it if you didn’t have a Chinese legal entity. This has changed over the time and now you can easily get a .cn domain, no matter where your company comes from, just providing a copy of your Company’s ID. As the Chinese international top level domain, your brand might be perceived as having a strong presence in China and might also bring some trust
– On the other hand, we have the .COM domain. Chinese Internet users are increasingly getting used to this domain. Major Ecommerce platforms like Tmall.com, JD.com or Sunning.com may bear much of the blame for this. It can be very good for foreign companies trying to sell their products in the Asian giant to have a .com domain as it might help to highlight the international feel of the brand
– .COM.CN is the ugly duckling in the middle still in use by many brands mixing the good things from the previous mentioned domains, but without reaching their full advantages. In any case it can also be a good solution.
Which language should I use?
Another point to think about is the language to be used. Does your brand have a Chinese name? Then you can also use its pinyin term. Pinyin is the romanization system for standard Chinese: Chinese search engines recognise the pinyin words in the URL and then link them to what they stand for in Chinese characters in order for the website not to lose coherence.
Our advice?
Don’t get crazy about the domain, they are usually not that expensive. So, in case you can afford it, try to get the three of them (.com, .cn and .com.cn), plus their pinyin variants and redirect them to the main one; depending on your strategy.

8 – CONTENT. DON’T GET LOST IN TRANSLATION
It is important to know very well your main target markets as the language will differ depending on it. It might be obvious to mention it, but it wouldn’t be the first time that a company’s target consumer is in Hong Kong, Taiwan or Macao and the language used for the website translation was simplified Chinese instead of traditional Chinese and the other way around. That is a major and silly mistake that takes a long time to revert.
I don’t want to mention either the fact that a Google translated web does not help at all, but I am doing it because I have seen too many. It is mandatory to let a professional team take care of the translations. In 2 Open we separate this process in three parts:
- Translation, interpreting the main message that the customer wants to transmit to the final customer, done by a marketing professional in our team
- External review, done by a professional translator outside the team
- Final review, done by another marketing professional in our team
You might not believe it, but in certain cases we still get minor complaints. This is because Chinese language can be interpreted in many different ways. Therefore translations are always a difficult point in the list.
Is Customization a mandatory requirement?
Let’s not forget about the Chinese cultural customization. Website localization embraces translating and localizing a site into different languages making sure all content (text, images and videos) is translated correctly in an accurate, cultural and technical manner.
As stated before when talking about content, we are also talking about images and videos. There are no written rules and it has similarities to the domain section we discussed above. There are brands like Nike or Zara that prefer to maintain their international feel using western models in their multimedia strategy. Many young Chinese users welcome this method, but not all of them. Depends on the strategy you want to follow.

9 – PAYMENT OPTIONS. CREDIT CARDS? NO, THANKS
In the previous post, we wrote about the BATs (Baidu, Alibaba and Tencent). In China, the online payments market is currently dominated by two of these two tech giants – Alibaba’s Alipay and Tencent’s WeChat payment with 49.2% and 20% market share respectively.
These companies try to increase their market share by adding more brands and merchants within their ecosystem; something that both companies effectively handle. Also cash is king, as cash on delivery holds a strong position. The fast and vast adoption of electronic payments via mobile is likely to counter this trend in due time.
It is actually China and not the US at the leading edge of the trends towards mobile payments technology. Just for putting an example, both WeChat and Alipay have long used the now famous QR codes to let Chinese netizens pay for purchases and transfer money. It seems they have jumped over some natural technological development processes. This kind of behaviours can be quite normal in undeveloped countries that start to grow very rapidly.
What happened is that they adopted the mobile payment technologies even before implementing some existing ones as a huge percentage of the Chinese population accesses the Internet via mobile devices.
Another tip?
Get ready to integrate Alipay in your website as first and mandatory option. And seeing how fast Tencent WeChat payment is growing, that would be your second natural option.

10 – SEO
Once your website is ready, you will need to submit it to Baidu creating a Baidu Webmaster Tools account (only available in Chinese). That way Baidu will be able to index the site properly and your great Chinese adventure starts!
Search engine optimization done in Baidu is not so very different as the one you could do for Google. Anyway, we would like to note a few differences I think you need to know:
– Meta description – unlike Google and Bing, Baidu still uses Meta descriptions as a ranking factor. Keyword targeted description match users’ queries and their demands, which would help with the click through rate (CTR).
– Indexation – Baidu’s web crawling bot, Baiduspider, is not as advanced as the one from Google. As a result, you will need to help Baiduspider to discover and index your pages in different ways. Without mentioning that you can go to sleep and wake up with huge traffic losses or de-indexed pages usually caused by a penalization. Be careful what you do!
– Link building – On Baidu, it is not about the quality of the publishers’ website, it is more about the unique relevancy of the content (as it relates to your content) and the quantity of links to your pages. Baidu penalizes duplicate content and it also disallows irrelevancy. Authority and quality of the publisher is not that important (for now). In short, the more the merrier as long as it is not duplicate.
– Baidu services – Baidu offers a lot of different products apart of Search; use them and leverage their integrated marketing power. The most useful are Baidu Zhidao (questions and answers service) and Baidu Baike (Wiki service), but there are tons of other services that might be helpful to increase brand awareness and for content creation.

OTHER ASPECTS
As for the tracking, most people use Baidu Tongji and/or Google Analytics. Yes, you read it well; Google Analytics still works in China and it is the only Google service that still does. You will find many detractors, but for what we have seen there is no huge discrepancies between the data collected by both systems (usually not higher than 5%). And Google Analytics has more functionalities than Baidu Tongji.
It is also important to mention the typography. Chinese language is not easy to read due to the difficulty associated to its typography. With 40,000 characters, they are divided in strokes which amount can vary between 1 and 60. Therefore the font size should be at least 12px.
At 2 Open, we would be pleased to help you.Take the advantages the Chinese market offers.
With the cooperation of our Digital Marketing and Ecommerce Agency, China will be at your fingertips.
Do not hesitate to visit us We´d loved to hear from you!
This article has been edited by Paula Vicuña, from 2 Open.
10 things you need to know to Build a Chinese Website (Part 1)
When planning to enter the Chinese market, one of the main points in every marketing plan should be the creation of a website that focuses on the Chinese consumer.
Naturally, there are some questions that come to mind…
- What are the differences between a western and an eastern website?
- What are the aspects that I have to keep in mind in order to trying to attract Chinese consumers?
- Would it be a good idea to just duplicate and translate my current content?
All of the above can be summarised in one question; what do I need to do in order to create a great website that will have the potential to reach the 675 million China internet users?
In this series of posts, we will try to give you some tips that will help you create a website for the Chinese market that will appeal to Chinese consumers and also match the style, tech and literary attributes of eastern consumers.
1 – Chinese Web Design – What the …???
When we look at a Chinese website, the first feeling we get is confusion… Language, structure, content … We can´t find anything similar to Western websites based (lately) on cleanliness and simplicity. Our China web design must be adapted not to our tastes, it must match Chinese consumer design taste.
If you have not navigated through Chinese websites maybe you don´t completrly understand what I mean. You´ll see easily the difference with these two examples. Taobao and Ebay, two B2C marketplaces (or C2C) from east and west.
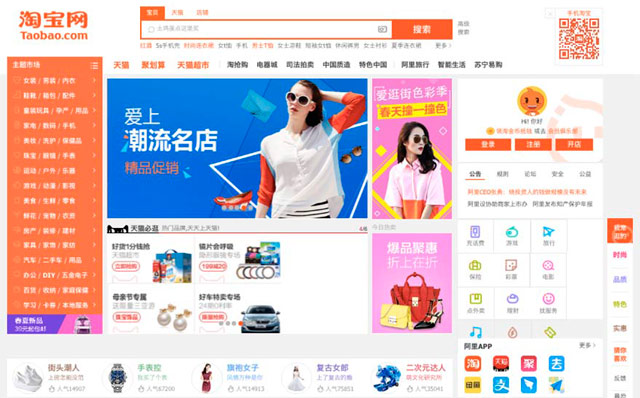
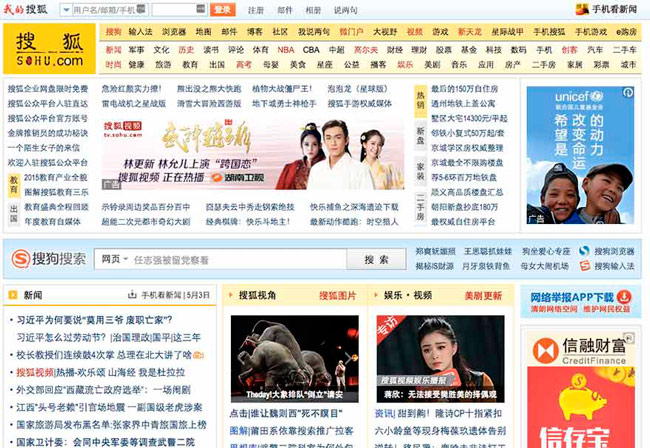
China Web Design Example – Taobao Home Page
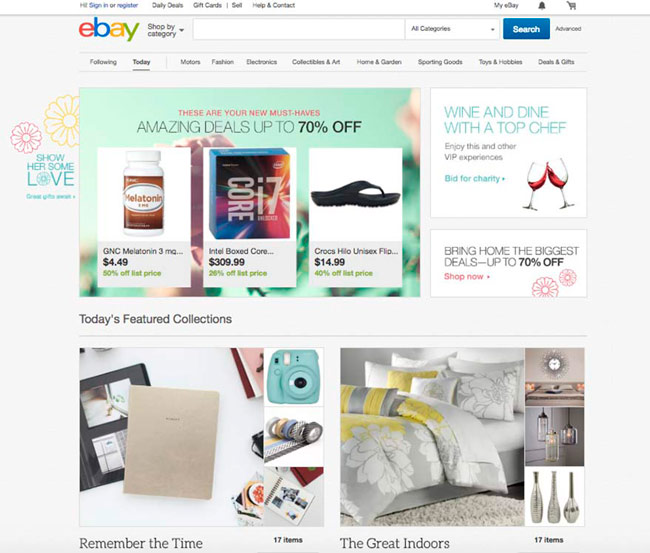
Western Web Design Example – Ebay Home Page
Can you appreciate the difference in style, design, structure? I bet you do…
We can see a lot of information on Chinese site in contrast to the cleanliness and simplicity of the western site.
Our experience creating websites for the Chinese market has shown us some key points to understand and get advantage:
- Chinese websites use many more elements and are much more colorful than Western.
- Chinese language is different. It seems obvious… but there are things we have to consider about Chinese language such as:
- There is not a capital letter in Chinese
- There are no spaces between characters
- Chinese characters are far more dense than our letters
- Chinese sites use a lot of animation, flashing texts and banners. This is clearly the opposite to our western websites where movement is disappearing. The reason can be it’s much harder to grab attention using fonts in Chinese than it is with western languages.
2 – User experience… Do they have any good one?
We have just seen as websites in China seem much more complex than we are used to. We might think that the user experience will be a nightmare, but Chinese user is so accustomed to information under this structure as we are to the western structure.
Chinese user is concerned about usability and user experience, but is used to webpages so busy usually does not care how the site looks. However the trend is towards simplicity and clarity on web pages. In a more European style.
Where is (link) Wally?
Some of the highlights on Chinese websites regarding to navigation are:
- Chinese websites have a big number of links, however Chinese users do not like this system. This can be given by the low load speed internet in China.
- All this links use to open in other new windows. Why? Again it’s mainly an issue of speed. Internet access in China is generally slow, users have gotten used to opening new links while waiting for a page to load.
- Keyword search box as a navigate tool. Link system is not comfortable for users because they can be lost due to the big amount of links. For this reason, on Chinese websites keyword searches have to be really efficient, and the search bar must be top accessible.
3 – Hosting & ICP. DIstance matterS
The one who said that, in internet there is no distance, did not know about China. If you are not (legal and/or physical) in Mainland China, easy staff like finding the right hosting can became a little bit more complicated.
Let´s start from the beginning, one of the most common questions when we are going to create a China site is should we host our website within or outside China? Is there is a big difference? The answer is very clear, as far as possible we should try host the web in Chinese Mainland, and we will try to explain why.
China network structure is not the best, which makes the websites loading speed not the most appropriate. By hosting our web outside China this problem becomes much more serious.
Okay, so we are clear, we should host our website in China, now what? We must apply for a number of ICP (Internet Content Provider) to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China. This is the ICP license that will allow our site to stay in Mainland China. Only companies with a physical presence in China can apply for this license (which usually see in the footer of the sites, as in our case).
For companies that do not have a legal entity in China, we do recommend looking for hosting solutions in Hong Kong, which can limit the problem of loading speed and make our site more accessible for the Chinese user.
Now that we talk about speed, even though the main problem affecting the same be the hosting (inside or outside) there are also other factors that can make our web go slower (and we have seen that it is a key point in China) as can be:
• Website images are not size optimized
• Poorly code in our website
• Low hosting quality (even inside Mainland China)
• Our site is using services blocked in China (Google Fonts, Google Maps, Twitter, Facebook, etc…) which prevents the page from loading
4 – Did you say… services blocked? … the Chinese Great Firewall
China not only has a huge physical walls to defend themselves (in the past). China also has a large digital wall, the Great Firewall. Originally known “Golden Shield Project” but ironically nicknamed Great Firewall, it is a censorship and surveillance project initiated by the Chinese Ministry of Public Security in 2003.
This project acts as a digital censor and block all websites that do not meet the content requirements that marks the Chinese government.
Here you can see some more information about how the censorship works.
Among other things, Chinese Internet censorship censored webpages that have content that include; news sources cover topics considered that are defamatory against China: such as police brutality, Tiananmen Square protests of 1989, freedom of speech, Taiwan Government, Dalai Lama or the Tibet Independence Movement International …
These sites are banned or are indexed to a lesser degree, if at all, by some Chinese search engines and have significant impact on search results.
As a result of this control in China they are blocked pages as usual for us as Google, Twitter or Facebook (it does no matter how much Mark go jogging in Tiananmen). Although great firewall control is easy to jump (using a VPN, for example) the difficulty of accessing these pages has made their use and popularity is low.

Stop laughing Mark. It´s not gonna happen
This means we need to be very careful with our website content, try to be sure to avoid Great Firewall content restrictions and not to use third party banned platforms like Google (Google Maps, Google Fonts), Facebook or Twitter.
5 – New Players & New Rules
So, no Facebook or twitter, how am I going to promote my website? China has a digital ecosystem different of everything we are use to. Surely you’re wondering how you survive without some of the usual promotional tools. Natural positioning in Google, PPC Adwords campaigns, promotion of content on social networks like Facebook or Twitter …
In China you will find new players who have occupied these gaps and in some cases, created new niches. These new players have taken advantage of the absence of foreign competition (Facebook, Google …), its adaptation to Chinese culture and peculiarity and in some cases even a strong government support.
These actors we found some “copycat“, certified copies of known systems, such as:
- Baidu, the Chinese search engine par excellence (suspiciously similar to Google)
- Weibo, the microblogging service (suspiiiiciouuusssslyyy similar to Twitter)
- Youku, video service (guess who it is similar?)
We also have WeChat, the jewel of the crown and the mobile app (almost an OS) that includes messaging, payments, calls, moments … and which we discussed in detail in another post.
For our website to be inside China digital life it must be adapted to the rules of these actors, common in the dailylife of the Chinese consumer.
So, who are the big guys that you need to be friend of?
As soldiers in a war, most of these tools fall into three large “armies”. These three groups are known as the BAT and are in constant battle to dominate the Chinese digital ecosystem.

Who is going to win this war?
In short, Baidu holds commanding market share over search. Alibaba holds to the same power over e-commerce. Tencent is the dominant player in social media. But they are constantly trying to invade their territory, in a very interesting war for any fan marketing.
One of the commonalities of the BAT is a full support of the government, together with its dominant position in the market, makes this status quo is difficult to change.
What does it means for our website? We need to adapt our communication to this new players, generating our social media activity through Wechat, optimizing our SEO for Baidu or 360, uploading our videos in Youku, adding sharing actions in our content with Chinese social platforms… anything we use to do in our occidental site does not help us here and can be even negative for our goals. As we have seen, if we keep on using tools like Facebook (post sharing options for example) we can be blocked by the Great Firewall.
Do you want to know more? Sure? CHECK THE SECOND PART OF THIS POST HERE
References:
http://www.china-briefing.com/news/2015/05/22/best-practices-launching-china-website.html
https://econsultancy.com/blog/67466-why-do-chinese-websites-look-so-busy/
http://www.latmultilingual.com/build-localized-chinese-website/
Sources:
http://www.freepik.com/free-vector/screen-with-a-website-and-icons_847180.htm
http://www.freepik.es/vector-gratis/trabajador-llorando_834598.htm
The Great Firewall: a barrier for foreigners who live in China
China is a very attractive country, rich in culture and full of traditions that appeal to most foreigners, it is also a place that offers considerable rewards for those who are seeking business opportunities. Despite its attractiveness there are some cultural barriers every foreigner has to overcome if they are planning to live in China, and these could sometimes turn out to be quite exasperating. In order to get a regular life in China, a “lǎowài” (老外term used by Chinese to refer to foreigners) has a few things to keep in mind, visas, language food and the business cultural differences, etc.
Apart from these issues, one of the greatest problems “lǎowài” face is Internet censorship. In this country there is a great firewall that blocks many foreign websites. In theory, this firewall was created with the objective of avoiding citizens’ protests against government and thereby they can filter all the content that is not suitable for the government’s interests, in a way they are trying to protect their citizens from unsuitable foreign media. Many of the websites with the highest traffic from the rest of the world cannot be accessed from the people’s republic of China. Webpages like: Google, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram among many others are not accessible with a conventional connection.
Some of these webpages have their own Chinese versions and are used by the Chinese community. Even though they do not have exactly the same functionalities and characteristics, here are some of the most famous ones with their Chinese counterparts, of course there are many more examples, but could be considered the most important ones:
| Youtube |
Youku
|
Twitter |
Weibo
|
Facebook |
Renren
|
Google |
Baidu
|
Ebay |
Alibaba /Taobao /Taobao
|
Amazon |
JD.com
|
It is practically unthinkable for a “lǎowài” to have to leave all the social networks and other webpages that he/she has been using for years and start using the Chinese versions. Luckily, there is one option in order to access to all the forbidden pages, without having to travel outside of Mainland China. The solution is a VPN (Virtual Private Network), which allows you to connect virtually to another network, in other words, when you connect using a VPN you are basically borrowing a server from another country, which tricks your computer into thinking it is located in that other country. As you do not seem to be connected from inside Mainland China, there is no firewall that prevents you to connect to all the desired webpages.
It is worth noticing to which country you are connecting to due to own governmental regulations, some countries also have restrictions that vary from blocked webpages to available downloadable content. Nowadays there are many companies offering VPN services. Here is a comparison between the most used providers in the market:
|
Astril |
PureVPN |
ExpressVPN |
VyprVPN |
|
| Speed |
Very Fast |
Fast |
Fast |
Fast |
| Price per year |
$69.95 |
$49.92 |
$99.84 |
$89.16/$106.92 |
| Simultaneous connections |
2 |
5 |
2 |
2/3 |
| Free trial |
7 days |
3 days |
30 days |
3 days |
| Servers |
280 |
500 |
100 |
700 |
| Supports |
Mac Os / iOS / Windows / Android / Linux |
|||
The great firewall is updated regularly, so there might be unable webpages one day that were working perfectly on the previous day. This is a reason for the VPN providers to stay on alert to those changes from the Chinese government. These are not the only VPN out there, there are a lot more VPN providers on the web, in case you feel adventurous. Lastly we would also advice you to respect governmental laws and regulations and also try the Chinese versions of your favorite app, and/or websites, who knows, you might end up liking it better.
This Article was edited by Andres Arroyo Olson from 2Open.
https://www.purevpn.com/order/
https://www.expressvpn.com/es/order
https://www.goldenfrog.com/ES/vyprvpn
http://startuplivingchina.com/best-vpn-for-china/
http://www.saporedicina.com/english/vpn-how-to-access-facebook-in-china/
http://blogthinkbig.com/que-es-un-vpn